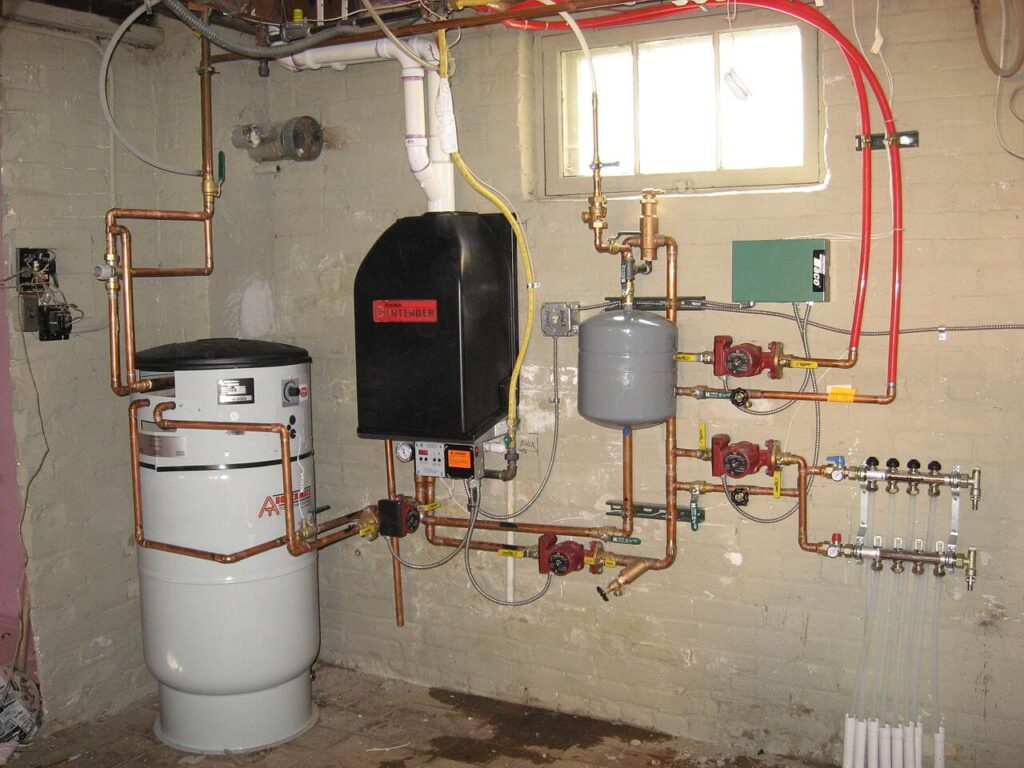

Boilers & Heating Systems
Get Plumbing Services Now
Forced Air Heating Systems
Advantages
– Easy installation: Electric heating systems are relatively simple to install, making them suitable for both new construction and retrofit projects.
– Individual room control: Electric baseboard heaters and other electric heating units can be controlled independently, allowing for customized temperature settings in different areas.
– No combustion byproducts: Electric heating systems do not produce combustion byproducts such as carbon monoxide, making them safer in terms of indoor air quality.
Disadvantages
– High operating costs: Electricity is often more expensive than other energy sources, resulting in higher heating bills.
– Limited efficiency: Electric heating systems may be less energy-efficient compared to options like natural gas or geothermal heat pumps.
– Lack of central heating: In larger spaces, multiple electric heating units may be required to adequately heat the entire area, leading to higher installation costs.
Hydronic Heating Systems
Advantages
– Energy efficiency: Hydronic systems are known for their energy efficiency, as they transfer heat directly to objects and people in the room.
– Quiet operation: Radiant heating systems operate silently, without the noise associated with forced air systems.
– Comfortable indoor environment: Radiant heat creates a cozy and consistent temperature, with no drafts or cold spots.
Disadvantages
– Higher installation costs: Installing hydronic systems, particularly in existing buildings, can be more complex and expensive compared to forced air systems.
– Slow response time: Hydronic systems may have a slower response time compared to forced air systems, as they rely on the gradual transfer of heat.
– Maintenance requirements: Hydronic systems require regular maintenance to ensure proper operation and prevent issues such as leaks or corrosion in the piping.
Geothermal Heating Systems
Advantages
– High energy efficiency: Geothermal systems utilize renewable geothermal energy, resulting in lower energy bills and reduced environmental impact.
– Long-term savings: Although installation costs may be higher, geothermal systems offer long-term savings through reduced energy consumption and lower operating costs.
– Durability: Geothermal systems have fewer moving parts than traditional HVAC systems, leading to fewer maintenance issues and a longer lifespan.
Disadvantages
– High upfront costs: The initial cost of installing a geothermal system can be significant, particularly for drilling or excavating the ground loop.
– Site requirements: Geothermal systems require sufficient space for the installation of ground loops, which may not be feasible in all locations.
– System complexity: Geothermal systems involve complex components such as heat pumps and underground piping, requiring specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance.
Get Plumbing Services Now
Some key terms to watch out for when considering different types of heating systems:

AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency)
A measure of how efficiently a furnace converts fuel into heat over the course of a heating season. Higher AFUE ratings indicate greater efficiency.

SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio)
Whether you're dealing with a clogged drain, cracked or chipped sink surface, or corrosion/rust issues, our team can provide prompt and efficient sink repair services. If a replacement is necessary, we offer a variety of sink options and will handle the installation process with precision and care.
Heat Pump
A device that transfers heat from one place to another, typically used for both heating and cooling purposes.
Boiler
A heating appliance that uses water or steam to distribute heat throughout a building.

Radiant Heating
A heating system that delivers heat directly to the floors, walls, or ceilings of a building, rather than through ducts or vents.

Thermostat
A device used to regulate the temperature of a heating or cooling system.
Ductwork
The network of channels used to distribute heated or cooled air throughout a building in a forced air heating or cooling system.
Zoning
A method of dividing a building into separate areas or zones, each with its own thermostat and heating/cooling controls, to optimize comfort and energy efficiency.
Geothermal Heat Pump
A type of heat pump that utilizes the stable temperature of the earth to provide heating and cooling for a building.

Energy Star
A certification program that identifies energy-efficient products, including heating and cooling systems, to help consumers save money and protect the environment.
Heat Exchanger
A component of a furnace or boiler that transfers heat from the combustion process to the air or water being heated.

Humidifier/Dehumidifier
Devices used to add or remove moisture from the air in a building, which can impact indoor comfort and air quality.
Our All Services
- Boilers and Heating Systems
- Commercial Plumbing Solutions
- Drains
- Emergency Plumbing Services
- Faucet and Sink Services
- Garbage Disposals
- Gas Line Services
- Leak Detection
- Outdoor Plumbing Solutions
- Piping & Re-piping
- Plumbing Repairs
- Sewer Services
- Showers & Toilets
- Water Heaters
- Water Line Maintenance
- Water Treatment Systems
+1 (888) 695-0243
Contact the Call Now Plumbing to schedule a service call.
Be prepared to provide help about the problem.
Don't let a plumbing emergency disrupt your life.
Call Now Plumbing to resolve your plumbing crisis with professionalism and care.